Facing wage garnishment can feel overwhelming, especially when it impacts your ability to cover essential expenses. If you’re asking, “How do I challenge a wage garnishment in Florida?” here’s what you need to know.
To challenge a wage garnishment in Florida, you can file a written objection with the court, claim an exemption to protect part of your income, request a garnishment hearing, or negotiate a payment plan with the creditor. Filing for bankruptcy is also an option to stop garnishment immediately.
With decades of experience helping individuals regain financial control, our team at DebtBusters understands the garnishment process and the steps needed to protect your income. Below, we provide a detailed guide to challenging a wage garnishment and regaining control of your finances.

Step 1 – Review the Wage Garnishment Notice
The first step in challenging a wage garnishment is to carefully review the notice you receive from the court or creditor. The notice provides essential details about the garnishment, including the amount being garnished, the creditor involved, and your rights.
Key Information to Look For
- Creditor’s Name and Amount Owed: Ensure you recognize the debt and verify the amount owed.
- Garnishment Amount: Check the percentage being garnished to ensure it does not exceed federal or state limits.
- Timeline to File an Objection: The notice should indicate the deadline to file an objection, often within five to ten business days of receiving the notice.
Understanding the details in your garnishment notice will help you identify any inaccuracies or legal grounds for challenging the garnishment.
Step 2 – Determine Your Legal Grounds to Challenge the Garnishment
Not all wage garnishments are eligible for objection, so it is essential to identify if you have valid legal grounds for challenging the garnishment. Common reasons to challenge a wage garnishment include incorrect debt information, undue hardship, or exemptions under state law.
Common Grounds for Challenging Garnishment
- Incorrect Debt Amount: If the debt amount is wrong or you believe it was miscalculated, you can dispute it.
- Mistaken Identity: If you are not the correct debtor, you have grounds to challenge the garnishment.
- Procedural Errors: Garnishments must follow strict procedures. Any errors in the process can be grounds for objection.
- Financial Hardship: If the garnishment causes you significant financial hardship, you may be able to request a reduction or exemption.
Review your state’s garnishment laws to understand the specific exemptions or hardship protections available to you.
Step 3 – File an Objection with the Court
To formally challenge the wage garnishment, you need to file an objection with the court that issued the garnishment order. Filing an objection is a legal action that requires submitting specific documents and forms.
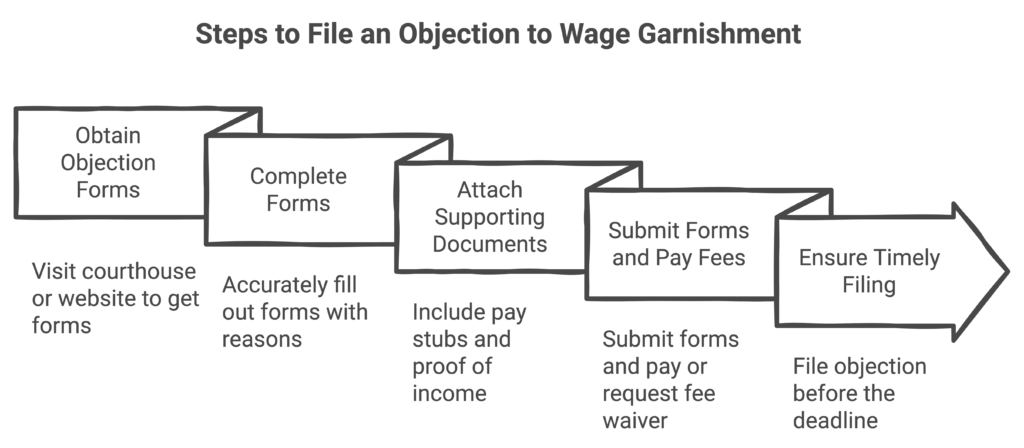
Steps to File an Objection
- Visit your local courthouse or court website to obtain the appropriate objection forms.
- Complete the forms accurately, stating your reasons for challenging the garnishment.
- Attach supporting documents, such as pay stubs, proof of income, or financial hardship documentation.
- Submit the completed forms and pay any filing fees (or request a waiver if you qualify).
- Ensure your objection is filed before the deadline indicated in the garnishment notice.
Common Documents Needed for Filing an Objection
Submitting your objection on time is crucial. Missing the deadline may forfeit your opportunity to challenge the garnishment.
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Garnishment Notice | Details of the garnishment |
| Pay Stubs or Income Proof | Shows impact on your income |
| Financial Hardship Statement | Explains financial hardship |
| Proof of Exemptions | Verifies eligibility for state exemptions |
Step 4 – Attend the Court Hearing
Once you file an objection, the court will schedule a hearing. This hearing is your chance to present your case and explain why the garnishment should be modified or stopped.
What to Expect at the Hearing
- Preparation: Bring copies of all supporting documents, including pay stubs, hardship letters, and evidence of any exemptions.
- Presentation: Be prepared to explain how the garnishment affects your ability to cover essential expenses and any legal grounds you have for challenging it.
- Judge’s Decision: After reviewing your case, the judge may decide to reduce, suspend, or cancel the garnishment.
Preparing thoroughly for the hearing increases your chances of a favorable outcome. A legal representative can be helpful during this process, especially if complex financial or legal details are involved.
Step 5 – File a Claim of Exemption if Eligible
Many states allow individuals to file a Claim of Exemption to protect a portion of their income from garnishment. If you qualify for an exemption due to financial hardship or dependent support, this claim can reduce or stop the garnishment.
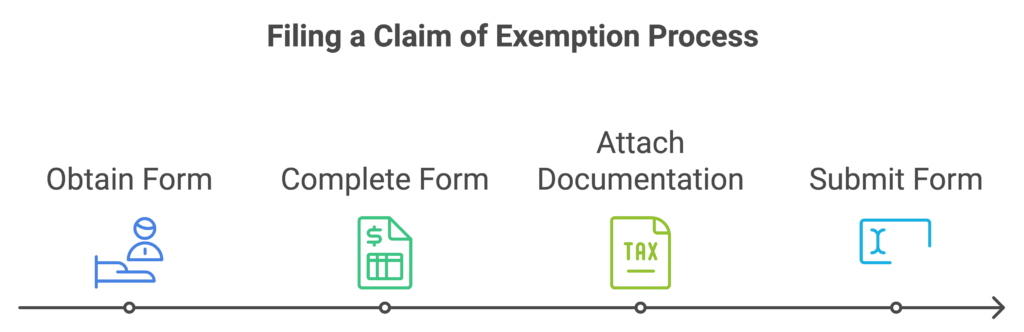
How to File a Claim of Exemption
- Obtain the Claim of Exemption form from your local courthouse or court website.
- Complete the form, detailing your financial situation and reasons for exemption.
- Attach required documentation, such as proof of income, dependents, or other applicable circumstances.
- Submit the completed form to the court and notify the creditor.
Filing a Claim of Exemption can be beneficial if garnishment makes it difficult to meet basic living expenses. Check your state’s guidelines for specific exemptions, as they vary widely by location.
Step 6 – Contact the Creditor to Negotiate
In some cases, it may be beneficial to reach out directly to the creditor to discuss a settlement or modified payment plan. Creditors are sometimes open to negotiation, as it allows them to recover funds without lengthy court proceedings.
Steps for Negotiation
- Contact the creditor or their legal representative and explain your financial situation.
- Propose a payment arrangement that is manageable for you.
- Request a written agreement if the creditor agrees to reduce the garnishment amount or suspend it in favor of a repayment plan.
Negotiating with creditors can provide relief without going through the court process and may even reduce the total amount owed.
Comparing Grounds for Challenging Wage Garnishment
Understanding the possible grounds for challenging wage garnishment can help you determine the best approach for your situation. This table summarizes common reasons for filing an objection and the supporting documents that may strengthen your case.
| Grounds for Challenge | Description | Supporting Documents |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Debt Amount | Dispute over debt balance or calculation | Debt statements, payment records |
| Mistaken Identity | Garnishment is for someone else’s debt | ID proof, other identity verification |
| Procedural Errors | Errors in garnishment procedure | Garnishment notice, court records |
| Financial Hardship | Garnishment prevents meeting basic needs | Pay stubs, budget statements |
| State-Specific Exemptions | Income qualifies for exemption | State exemption forms, proof of income |
Each of these grounds requires specific evidence to support your case. Gather documentation that clearly demonstrates your eligibility for an exemption or reduction.
Take Action to Protect Your Income
Facing wage garnishment can create significant financial strain, but you have the right to challenge or modify it if it is incorrect or causes undue hardship. By following these steps and acting quickly, you can protect a portion of your income and regain stability.
If you need assistance navigating the garnishment process or want expert guidance to protect your finances, contact DebtBusters at (866) 223-4395. Our experienced team is here to help you take control of your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my wage garnishment is eligible for challenge?
Garnishment may be eligible for challenge if there are errors in the debt amount, mistaken identity, procedural errors, financial hardship, or if you qualify for exemptions. Reviewing your garnishment notice and state laws can clarify your eligibility.
What is the deadline to file an objection to wage garnishment?
The deadline to file an objection is usually between five to ten business days from the date you receive the garnishment notice. Filing promptly is essential, as missing the deadline may limit your ability to challenge the garnishment.
What happens if my wage garnishment challenge is successful?
If your challenge is successful, the judge may reduce, suspend, or cancel the garnishment. This can provide you with immediate financial relief and help you better manage your expenses.
Can I file a Claim of Exemption to stop wage garnishment?
Yes, if you qualify based on state laws. A Claim of Exemption allows you to protect a portion of your income, often due to financial hardship or dependent support. Check your state’s specific guidelines to determine eligibility.
Do I need a lawyer to challenge wage garnishment?
Although a lawyer is not required, having legal representation can be helpful, especially for complex cases. A lawyer can ensure your objection is properly filed, represent you in court, and increase your chances of success.
What is the automatic stay and how does it help with garnishment?
If you file for bankruptcy, an automatic stay temporarily halts most collection actions, including wage garnishment. This stay provides immediate relief from garnishment, giving you time to explore long-term debt solutions.
Can negotiating with my creditor stop wage garnishment?
Yes, negotiating directly with your creditor may lead to a modified payment plan or reduced garnishment amount. Creditors are often open to negotiation if it ensures consistent payments without court intervention.