Reading Time: 6 Minutes
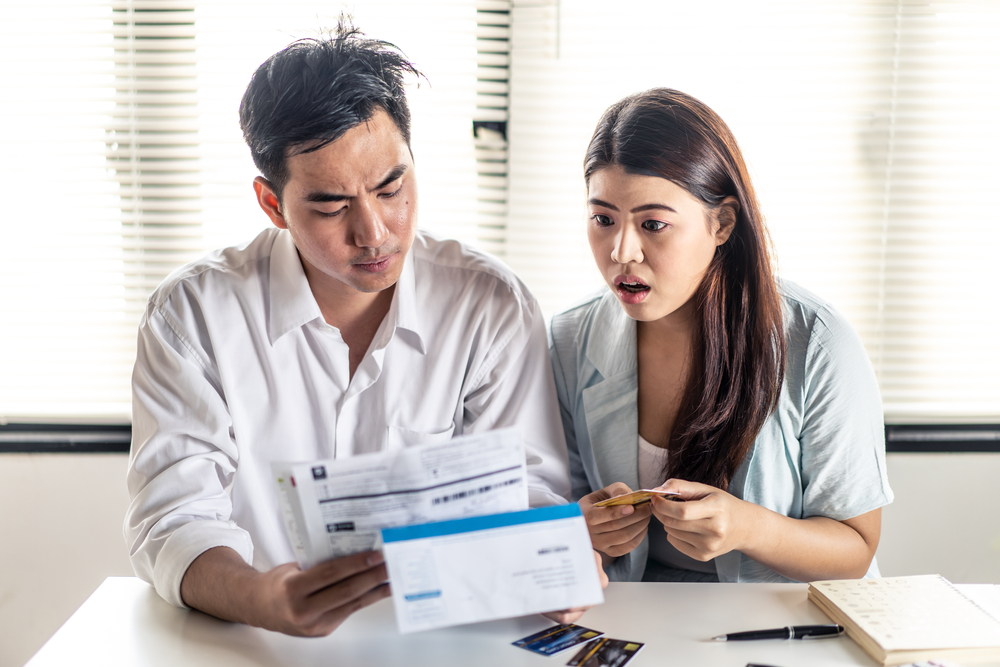
If you’re considering combining multiple debts into one loan, you may be asking: Do consolidation loans hurt your credit score?
Yes, debt consolidation loans can temporarily lower your credit score due to hard inquiries and opening a new account. However, over time, responsible debt management—such as reducing credit utilization and making on-time payments—can improve your score.
With decades of experience helping individuals rebuild their financial health, I’ve guided many through the pros and cons of debt consolidation. Below, I’ll break down how consolidation loans impact your credit and how to minimize any negative effects while improving your overall financial standing.
Key Takeaways
- Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan with one monthly payment.
- Options for debt consolidation include personal loans, home equity loans, and balance transfers.
- The impact on your credit depends on your financial habits and the type of consolidation you choose.
What Is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan, making it easier to manage payments. Instead of paying several creditors each month, you pay just one lender. This approach doesn’t erase your debt but can make repayment more efficient and less stressful.
The primary goal of debt consolidation is twofold:
- Simplify Payments: Replace multiple payments with one monthly payment.
- Lower Costs: Secure a loan with a lower interest rate to save money over time.
For example, if you have three credit cards with high-interest rates, consolidating them into a personal loan with a lower rate can reduce your overall interest payments and help you pay off your debt faster.
Types of Debt Consolidation Options
The best debt consolidation method depends on your financial situation. Here are the main options:
- Debt Consolidation Loans
- Personal loans designed for consolidating debt.
- Lower interest rates compared to most credit cards.
- Typically unsecured, so no collateral is required.
- Best for borrowers with good credit scores (670+).
- Home Equity Loans or HELOCs
- Use your home’s equity as collateral.
- Lower interest rates than unsecured loans.
- Risk of losing your home if you fail to repay.
- Balance Transfer Credit Cards
- Transfer multiple debts to a single credit card with a low or 0% introductory interest rate.
- Often includes transfer fees (usually 3-5% of the transferred amount).
- Ideal for borrowers with good to excellent credit scores.
- 401(k) Loans
- Borrow against your retirement savings.
- No credit check required, but reduces retirement growth.
- Risk of penalties and taxes if the loan isn’t repaid.
- Debt Management Plans
- Offered by non-profit credit counseling agencies.
- Consolidate debt without taking out a new loan.
- Creditors may agree to reduce interest rates, but you’ll need to stop using credit during the repayment plan.
How Debt Consolidation Affects Your Credit
Debt consolidation can impact your credit in both positive and negative ways, depending on how you manage it:
Positive Effects
- Lower Credit Utilization: Moving high credit card balances to a personal loan can lower your credit utilization ratio, improving your score.
- On-Time Payments: Simplifying payments can make it easier to pay on time, which positively impacts your payment history (the biggest factor in your credit score).
Negative Effects
- Hard Inquiries: Applying for a loan generates a hard inquiry, which can temporarily lower your score.
- New Credit Impact: Adding a new loan reduces the average age of your credit accounts, which may slightly decrease your score.
For example, if your credit score is above 740, you’re more likely to get favorable loan terms. Scores below 670 might result in higher interest rates, which could make consolidation less cost-effective.
Comparison of Debt Consolidation Options
When choosing a debt consolidation method, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each option. The table below summarizes the main differences:
| Method | Best For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debt Consolidation Loan | Borrowers with good credit | Lower interest rates, no collateral required | May not be available for bad credit |
| Home Equity Loan/HELOC | Homeowners | Low interest rates, higher loan amounts | Risk of foreclosure if unable to repay |
| Balance Transfer Card | High credit card balances | 0% introductory APR, easy application process | Limited promotional period, transfer fees |
| 401(k) Loan | Retirement account holders | No credit check, quick access to funds | Reduces retirement growth, tax penalties |
| Debt Management Plan | Struggling with credit cards | Professional negotiation, avoids new loans | Restrictions on new credit, monthly fees |
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right path based on your financial goals and resources.
Alternatives to Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation isn’t the only option. Here are some alternatives:
- Debt Settlement
- Negotiate with creditors to pay less than the full amount owed.
- Can hurt your credit but may be an option for severe financial struggles.
- Snowball or Avalanche Methods
- Pay off smaller debts first (snowball) or highest-interest debts first (avalanche).
- No new loans required, and you remain in control of your repayment strategy.
- Cash-Out Refinancing
- Homeowners refinance their mortgage to access cash and pay off debt.
- Can reduce interest but extends mortgage repayment terms.
- Bankruptcy
- A legal process to discharge debts when repayment is impossible.
- Severe impact on credit but provides a fresh start. Should be a last resort.
How to Decide if Debt Consolidation Is Right for You
Ask yourself the following questions:
- Do I have good credit? Borrowers with higher credit scores benefit most from low-interest loans.
- Will I save money? Compare your current interest rates with the new loan’s rate.
- Can I avoid new debt? Debt consolidation only works if you stop accumulating new debt.
Use tools like a debt consolidation calculator to estimate your savings and ensure consolidation is the right financial move. Check out resources like Consumer Financial Protection Bureau for more tips.
Tips for Successful Debt Consolidation
- Shop Around: Compare lenders for the best rates and terms.
- Create a Budget: Prevent overspending and ensure you can make payments on time.
- Read the Fine Print: Check for hidden fees or prepayment penalties.
- Commit to a Plan: Avoid new debt and focus on paying off your consolidated loan.
Why Choose DebtBusters?
At DebtBusters, we understand how overwhelming debt can feel. That’s why we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Whether you’re considering a consolidation loan, a debt management plan, or exploring alternatives, our team of experts will help you find the best solution for your financial future.
Take the First Step Today
Let DebtBusters help you take control of your finances. Contact us for a free consultation to explore your options and create a customized plan. Call us now at (866) 223-4395 or visit DebtBusters.com to get started.
Don’t wait—start your journey to financial freedom today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does debt consolidation work?
Debt consolidation works by combining multiple debts into one loan with a single monthly payment. This can simplify your finances and reduce interest costs if you secure a lower rate. It’s important to ensure the new loan is manageable and won’t lead to new debt accumulation.
2. Does debt consolidation hurt your credit?
Debt consolidation can temporarily lower your credit score due to hard inquiries and new accounts. However, making consistent payments can improve your score over time by reducing your credit utilization ratio and establishing a positive payment history.
3. What is the best way to consolidate credit card debt?
The best way to consolidate credit card debt depends on your credit score and financial situation:
- Use a balance transfer card for 0% APR offers (if you qualify).
- Opt for a personal loan with a lower interest rate.
- Consider a debt management plan if you need professional assistance.
4. Is debt consolidation the same as debt settlement?
No, debt consolidation involves taking out a loan to pay off debts, while debt settlement negotiates reduced payments with creditors. Consolidation is generally less harmful to your credit and more predictable.
5. Can I consolidate debt with bad credit?
Yes, but your options may be limited. Borrowers with bad credit might face higher interest rates or need to explore alternatives like secured loans or debt management plans.
6. What is the difference between secured and unsecured debt consolidation?
Secured debt consolidation uses collateral (like your home) to back the loan, while unsecured loans do not require collateral. Secured loans often have lower interest rates but higher risks, such as losing your asset if you default.