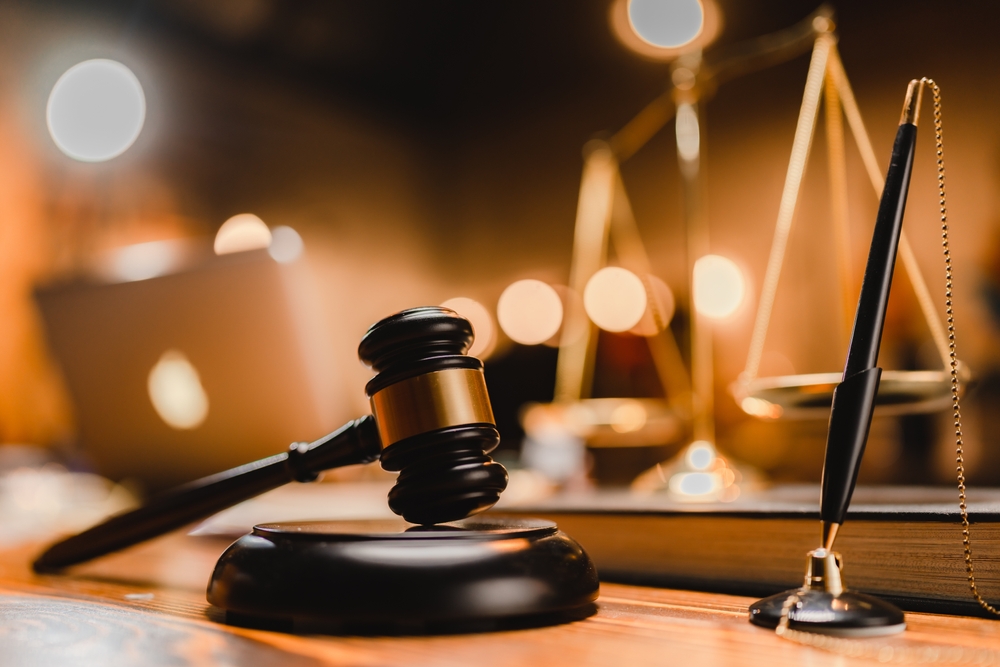
Filing for bankruptcy can be a powerful tool for individuals struggling with overwhelming debt, including those facing lawsuit judgments. Understanding how bankruptcy law can impact a judgment and the process involved in filing for bankruptcy in Nevada is crucial. This article will explore whether you can file bankruptcy on a judgment in Nevada, the types of judgments that can be discharged, and the steps involved in the bankruptcy process.
Understanding Judgments and Bankruptcy
What is a Judgment?
A judgment is a court order that determines the outcome of a lawsuit. If you owe money to a creditor and fail to pay, the creditor may file a lawsuit against you. If the court rules in favor of the creditor, a judgment is issued, which can lead to wage garnishment, bank account levies, or liens on your property.
Types of Judgments
Judgments can be categorized into several types, including:
- Money Judgment: A court order requiring the debtor to pay a specific amount of money to the creditor.
- Judgment Lien: A lien placed on the debtor’s property to secure the payment of a money judgment.
- Default Judgment: A judgment issued in favor of the creditor when the debtor fails to respond to the lawsuit.
Impact of a Judgment on Your Finances
Judgments can have severe financial consequences, including:
- Wage Garnishment: The court may order your employer to withhold a portion of your wages to pay the creditor.
- Bank Account Levies: The creditor can freeze and withdraw money from your bank account.
- Property Liens: A judgment lien can be placed on your real property, affecting your ability to sell or refinance. A judgment lien can transform an unsecured debt into a secured debt, which has significant implications for your financial situation.
Can You File Bankruptcy on a Judgment in Nevada?
Filing Bankruptcy to Discharge Judgments
Yes, you can file bankruptcy on a judgment in Nevada. Filing for bankruptcy can help discharge certain types of judgments, providing relief from the financial burden through a bankruptcy discharge. However, the dischargeability of a judgment depends on the debt’s nature and the bankruptcy code’s specifics.
Types of Judgments Dischargeable in Bankruptcy
- Credit Card Debt: Judgments resulting from credit card debt are generally dischargeable in bankruptcy.
- Medical Bills: Judgments for unpaid medical bills can be discharged in bankruptcy.
- Personal Loans: Judgments from personal loans are typically dischargeable.
- Collection Lawsuits: Judgments from collection lawsuits for unsecured debts can be discharged.
Non-Dischargeable Judgments
Certain lawsuit judgments are not dischargeable in bankruptcy, including:
- Child Support: Judgments for unpaid child support are not dischargeable.
- Alimony: Judgments for alimony payments remain in effect.
- Student Loans: Most student loan judgments are non-dischargeable unless you can prove undue hardship.
- Taxes: Judgments for most taxes are non-dischargeable.
- Fraudulent Debts: Judgments arising from fraudulent activities are not dischargeable.

The Bankruptcy Process
Filing for Bankruptcy
Filing for bankruptcy involves several steps, including:
- Consult a Bankruptcy Attorney: It is crucial to consult with a bankruptcy attorney to understand your options and determine the best course of action.
- Complete Credit Counseling: You must complete an approved course before filing.
- File the Bankruptcy Petition: Your attorney will help you prepare and file the bankruptcy petition and other required documents with the bankruptcy court.
- Automatic Stay: Once you file for bankruptcy, an automatic stay goes into effect, halting most collection activities, including wage garnishment and bank account levies.
- 341 Meeting of Creditors: You will attend a meeting with the bankruptcy trustee and your creditors to discuss your financial situation.
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 bankruptcy, or liquidation bankruptcy, involves selling non-exempt assets to pay off creditors. The remaining unsecured debts, including dischargeable judgments, are discharged, providing a fresh start.
Eligibility for Chapter 7
To qualify for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you must pass the means test, which compares your monthly income to the median income for a household of your size in Nevada. If your income is below the median, you qualify for Chapter 7. If it exceeds, you may need to file for Chapter 13 instead.
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Chapter 13 bankruptcy, or reorganization bankruptcy, involves creating a repayment plan to pay off debts over three to five years. This type of bankruptcy allows you to keep your property while repaying your debts through structured payments.
Eligibility for Chapter 13
To qualify for Chapter 13, you must have a regular income and meet the debt limits set by the bankruptcy code. This option is suitable for individuals who can pay monthly debt payments.
The Role of the Bankruptcy Court
Filing the Bankruptcy Petition
Filing the bankruptcy petition with the bankruptcy court is the first step in the process. The petition includes detailed information about your finances, debts, and assets. The court will review your petition to ensure it meets the bankruptcy code requirements.
The Bankruptcy Trustee
A bankruptcy trustee is appointed to oversee your case. The trustee reviews your petition, conducts the 341 meeting of creditors, and ensures that your case complies with the bankruptcy procedures. The trustee plays a crucial role in identifying potential issues and ensuring the process is conducted fairly.
Discharge of Debts
Once the bankruptcy case closes, the court issues a discharge order, which releases you from personal liability for dischargeable debts, including eligible judgments. The discharge order prevents creditors from taking any further collection actions on the discharged debts.

Impact of Bankruptcy on Judgments
Automatic Stay
The automatic stay is a powerful tool that goes into effect immediately upon filing for bankruptcy. It halts most collection activities, including wage garnishment, bank account levies, and property liens. This provides temporary relief and allows you to focus on the bankruptcy process.
Discharging Judgment Liens
While bankruptcy can discharge the personal liability associated with a judgment, it does not automatically remove judgment liens from your property. You may need to file a motion with the bankruptcy court to remove a judgment lien. Your attorney can help you navigate this process.
Addressing Secured Debts
If a judgment is secured by collateral, such as a car loan or mortgage, the underlying debt may not be dischargeable. In such cases, you may need to negotiate with the creditor to address the lien or reaffirm the debt to retain the collateral.
The Importance of a Bankruptcy Attorney
Legal Guidance and Representation
Hiring a bankruptcy attorney is essential for navigating the complexities of the bankruptcy process. An experienced attorney can help you understand your options, prepare necessary documentation, and represent you in court.
Services Provided by a Bankruptcy Attorney
- Initial Consultation: Assess your financial situation and discuss your options.
- Filing the Petition: Prepare and file the bankruptcy petition and accompanying schedules.
- Representation: Represent you at the 341 meeting of creditors and any subsequent court hearings.
- Negotiations: Negotiate with creditors and the bankruptcy trustee on your behalf.
- Guidance: Provide ongoing advice and support throughout the bankruptcy process.
Cost of Hiring a Bankruptcy Attorney
The cost of hiring a bankruptcy attorney can vary based on the complexity of your case and the type of bankruptcy you are filing. Chapter 7 cases generally cost between $1,000 and $2,500, while Chapter 13 cases can range from $2,500 to $3,500. Many attorneys offer payment plans to help manage the cost.

Alternatives to Bankruptcy
Debt Settlement
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount of debt owed. It can be a viable alternative to bankruptcy for those who can make a lump-sum payment or a series of payments to settle their debts.
Pros and Cons of Debt Settlement
- Pros: Can reduce the total amount of debt owed, avoid the stigma of bankruptcy, and potentially improve your financial situation more quickly.
- Cons: Can negatively impact your credit score, may result in tax liabilities on forgiven debt, and not all creditors may agree to settle.
Debt Management Plans
Debt management plans (DMPs) are offered by credit counseling agencies to help individuals manage their debt. A DMP consolidates multiple debts into a monthly payment, often with reduced interest rates and waived fees.
Benefits of Debt Management Plans
- Single Monthly Payment: Simplifies debt repayment by consolidating multiple debts.
- Lower Interest Rates: Credit counselors negotiate lower interest rates and fees with creditors.
- Financial Counseling: Provides ongoing financial education and support to help you manage your finances.
Debt Consolidation Loans
Debt consolidation loans involve a new loan to pay off multiple existing debts. This can simplify your payments and potentially reduce your interest rates.
Advantages of Debt Consolidation Loans
- Simplified Payments: Combines multiple debts into a single loan.
- Potentially Lower Interest Rates: May offer lower interest rates than credit cards or other high-interest debts.
- Fixed Repayment Schedule: Provides a clear timeline for repaying your debt.
Understanding Bankruptcy Procedures
Steps in the Bankruptcy Process
- Credit Counseling: Complete an approved credit counseling course.
- Filing the Petition: File the bankruptcy petition with the court.
- Automatic Stay: The automatic stay halts most collection activities.
- 341 Meeting of Creditors: Attend the meeting with the trustee and creditors.
- Discharge: The court issues a discharge order, releasing you from personal liability for dischargeable debts.
Common Misconceptions About Bankruptcy
- Bankruptcy is Only for the Financially Destitute: Bankruptcy is a legal tool designed to help individuals and businesses restructure or discharge debts, regardless of their financial status.
- All Debts Are Discharged in Bankruptcy: Not all debts are dischargeable in bankruptcy. Certain debts, such as child support, alimony, most student loans, and certain tax obligations, are not dischargeable.
Preparing for a Bankruptcy Filing
Gathering Necessary Documentation
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful bankruptcy filing. Gather all necessary documentation, including:
- Income Records: Pay stubs, tax returns, and proof of any other income.
- Expense Records: Bills, receipts, and statements for all monthly expenses.
- Debt Information: Statements from all creditors, including secured and unsecured debts.
- Asset Information: Document all assets, including property, vehicles, and personal belongings.
Completing Bankruptcy Forms
Filing for bankruptcy involves completing several forms, including the bankruptcy petition, assets and liabilities schedules, and a financial affairs statement. These forms provide a detailed overview of your financial situation and must be filled out accurately.
Filing the Bankruptcy Petition
Once all documentation is gathered and forms are completed, your bankruptcy attorney will file the petition with the bankruptcy court. This officially starts the bankruptcy process and triggers the automatic stay.
Life After Bankruptcy
Rebuilding Your Credit
After your bankruptcy case is discharged, focusing on rebuilding your credit is important. Steps to improve your credit score include:
- Making Timely Payments: Ensure all bills are paid on time.
- Using Credit Wisely: Apply for a secured credit card and use it responsibly.
- Monitoring Your Credit Report: Regularly check your credit report for errors and track your progress.
Financial Planning
Developing a solid financial plan can help you avoid future financial difficulties. Key steps include:
- Creating a Budget: Track your income and expenses to ensure you live within your means.
- Building an Emergency Fund: Save some of your income for unexpected expenses.
- Setting Financial Goals: Establish short-term and long-term goals to guide your spending and saving.

Conclusion: Handling Bankruptcy and Judgments in Nevada
Filing for bankruptcy on a judgment in Nevada can provide significant relief from financial burdens. Understanding the types of judgments that can be discharged, the bankruptcy process, and the role of a bankruptcy attorney is crucial for achieving a successful outcome. Whether you are dealing with wage garnishment, bank account levies, or property liens, bankruptcy can offer a path to financial stability.
If you are considering filing for bankruptcy and need expert guidance, contact DebtBusters for a free consultation with an experienced bankruptcy attorney. We can help you determine your eligibility and explore the best options for achieving financial relief.
Schedule your free consultation now!
Related Content: Debt Statute of Limitations in Nevada in 2024: Everything You Need to Know